Species Profile: The Blue Shark
The blue shark is the most heavily fished shark in the world. Find out why.
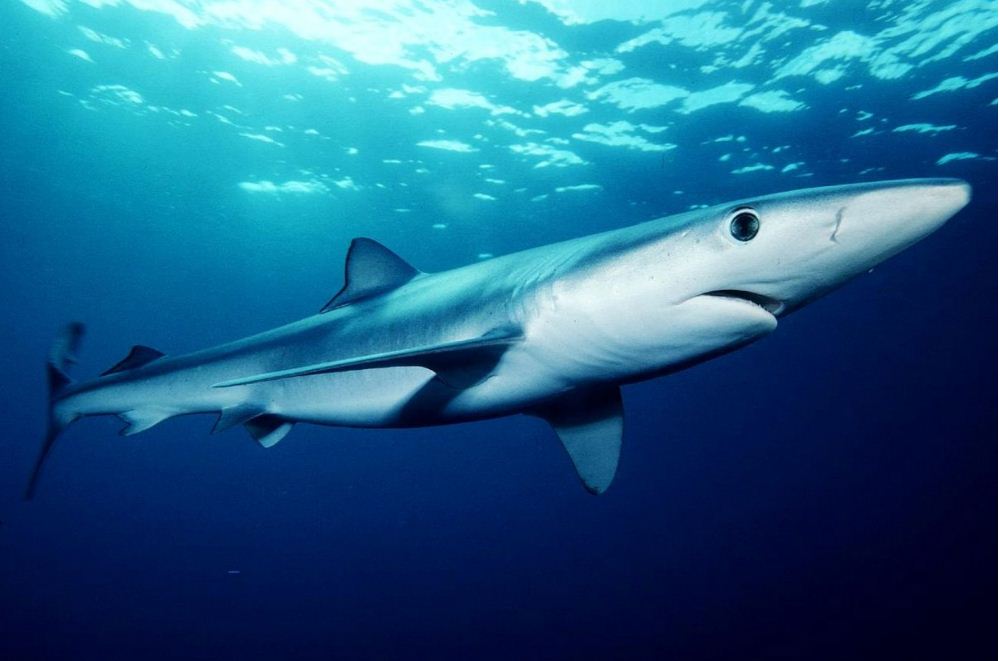
It’s no exaggeration to say the blue shark is one of the most beautiful sharks swimming in the earth’s waters today.
It stands out with its slim, elongated, torpedo-shaped body and beautiful swimming style. Sadly, this shark species is among the most highly fished sharks around.
Humans catch it for its fins, meat, oil, and as a display animal because of its beauty.
About 10 million blue sharks are killed by humans every year! As a result, this shark is listed as Near Threatened by the IUCN.
Blue sharks have a deep blue back with white underbelly, large eyes, and long pectoral fins. It has a particularly strong and unique sense of smell.
1) Scientific Name
Prionace glauca
2) Scientific Classification:
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Chondrichthyes
- Order: Carcharhiniformes
- Family: Carcharhinidae
- Genus: Prionace
3) Life Expectancy
Averagely 15/16 years in the wild.
4) Average/Maximum Length
The females of this species are slightly larger than their male counterparts.
Females usually grow up to 2.2 – 3.3 meters (7.2 – 10.8 feet) at maturity, and males 1.82 – 2.82 meters (6.0 – 9.3 feet) at maturity.
Some of the largest individual blue sharks found so far were up to 3.8 meters (12 feet) long.
5) Average/Maximum Weight
Adult blue sharks will weigh around 27 to 55 kg (60 to 121 lbs.) for the males and from 93 to 182 kg (205 to 401 lbs.) for the females. The heaviest reported weight so far was 391 kg (862 lbs.)
6) Maximum Swimming Speed
These are leisurely swimmers but fast too. They can move as fast as 24.5 m/h (40 km/h) in certain circumstances.
7) Interaction/Danger To Humans
The meat of the blue shark is edible though it has a high ammonia content. It is sold fresh, dried, salted, or smoked. People also use its skin for leather products, its fins are used for shark fin soup, and its liver oil for various commercial purposes.
Because of its beauty, blue sharks are frequently captured for game fish and are kept in captivity. Unfortunately, they rarely survive more than a few months in enclosed spaces.
Though the blue shark rarely encounters humans because of its pelagic habitat, it is considered as relatively dangerous. They may attack people and boats if their paths cross.
The blue shark is responsible for at least 4 fatal human attacks and about a dozen reported unprovoked attacks.
8) Reproduction Details
Despite their slender and sleek appearance, the blue shark has a very violent courtship process. The males bite the female sharks quite viciously. Luckily, the skin of the female blue shark is three time thicker than that of the male in order to prevent severe damage.
The blue sharks gives birth by viviparous reproduction. They have one of the highest birth rate among sharks: sometimes up to 135 pups in a litter. Gestation period is between 9 and 12 months.
Females mature at 5/6 years and males at 4/5 years old.
9) Diet/Hunting Pattern Of The Blue Shark
They have very jagged, comb-like pointed teeth in their upper and lower jaws. Combined with the ability to swim at fast speed, this shark can capture and feed on a variety of prey even some larger than itself.
Blue sharks have also devised some interesting hunting strategies. They can work together as a ‘pack’ to chase, herd, and catch a large quantity of prey.
Their preferred diet is squid, but they also eat other invertebrates, like the cuttlefish, pelagic octopus, lobster, shrimp, sea birds, crab, and a variety of bony fish. Blue sharks also, they eat smaller sharks.
Killer whales, tiger sharks, and great white sharks hunt the blue whale.
10) Alternative Names
- Blue whaler
- Blue dog
- Great blue sharks
- Great blue whalers
11) Population And Conservation Status
In addition to heavy overfishing, blue sharks get caught by longline and dragnet fishing fleets. They’re also caught for sport and game.
For now, several countries like Australia, Canada, and the USA have risen to implement restrictions and conservation projects for the blue shark and other pelagic sharks.
But, this shark is still a target of the shark fin soup industry, so it remains ‘Near Threatened.’
12) Ancestry And History
The blue shark is a species of requiem sharks. These sharks are characteristic for their migratory lifestyle and for bearing live young. They prefer the deep temperate and tropical oceans of the world.
Though most requiem sharks exhibit a number of common features, each one is still unique. The most common requiem sharks are the blue shark, tiger shark, white tip reef shark, dusky shark, and daggernose shark.
Even though their numbers suffered heavily over the years due to human activities, they still exist in most of their original, historic habitats.
13) Distribution And Habitat
This shark species lives worldwide from the surface to about 350 meters deep in temperate and tropical waters. The only waters they don’t inhabit are around the polar areas.
Populations in temperate seas will often approach the shore, but those in tropical waters live at greater depths. You can find them off the coast of every continent apart from Antarctica. Their distribution is as wide as from Norway to Chile, and from New England to South America.
Blue sharks like to move in schools of many individuals. Interestingly, they segregate themselves according to age, size, and sex. As such, you can find male only or female only groups.






